Practice Lab for the BSN Program: Plans for Growth
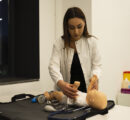
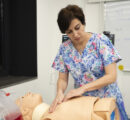
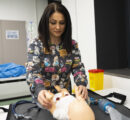
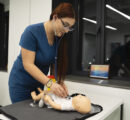
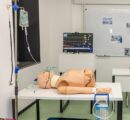
2 min readYEREVAN, Armenia — The Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program faculty members at the American University of Armenia’s (AUA) Turpanjian College of Health Sciences (CHS) have launched a small-scale practice lab in the University’s Najarian Center to support the learning of current BSN students, enhance their clinical skills, and apply evidence-based practice. The nursing faculty at CHS has been proactive in adopting the latest advancements in skills teaching, working with mid-level fidelity types of mannequins, and utilizing high-level critical thinking patient care scenarios to equip the future nursing workforce with the latest up-to-date competencies. The BSN program is actively seeking funding opportunities to support the lab’s expansion into a full-scale simulation lab.
Simulation has been proven to be one of the most effective learning and teaching methods in various professions, specifically in nursing education. With recent advancements in education, simulation has gained momentum in providing an experiential, safe learning environment for multiple disciplines to achieve desired specific student learning outcomes. As per the latest guidelines of the Association of the American Colleges of Nursing, the future nursing workforce should be able to demonstrate essential competencies that are contemporary to current advances in healthcare.
Therefore, simulation experiences are essential to clinical education, providing valuable augmentation to direct and indirect care within healthcare settings. These offer an effective, safe environment for learning and demonstrating competencies. A landmark study conducted by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing concluded that for pre-licensure students, “substituting high-quality simulation experiences for up to half of traditional clinical hours produces comparable end-of-program educational outcomes” (Hayden et al., 2014, p. S3).
Overall, strengthening nursing’s unique and propelling workforce with updated standards of care and practice is directly linked to enhanced patient care outcomes. A groundbreaking study by Cheung RB et al. established that the educational level of nurses in hospitals was associated with patient mortality: for every 10% increase in the proportion of baccalaureate-prepared nurses, hospital mortality rates decreased by 5%. Simulation practice helps raise the level of standardized nursing practice and has become an essential component of bachelor of science-level nursing education.
The AUA Turpanjian College of Health Sciences works actively to improve population health and health services in Armenia and the region through interdisciplinary education and development of health professionals to be leaders in public health, nursing, health services research and evaluation, and health care delivery and management.